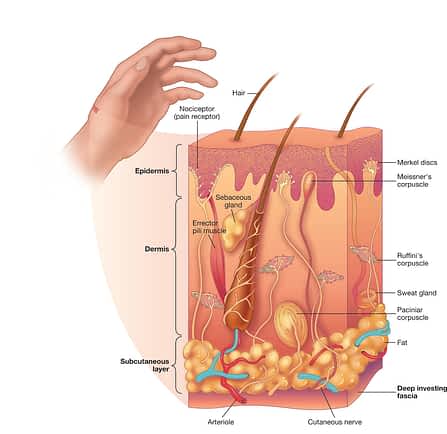
Keeping your skin healthy is important so that it can perform all the functions it was designed to perform. But what role does skin, our largest organ of the body, actually play? Here are six important physiological and biochemical functions that skin has for the body.
1. Regulating Temperature (Thermoregulation).
You’ve probably noticed your skin gets red when you are hot, and paler when you are cold. This is because the skin is trying to keep the internal body at a desired temperature of 98.6F or 37C. It does this sending more blood to the skin to diffuse heat to the atmosphere when you are hot and by holding more blood in the core (away from the skin) when you are cold.
Another way your skin helps regulate temperature is by secreting sweat. Sweat then evaporates on the skin’s surface which has a cooling effect. This also causes your body to lose water which can cause dehydration if your do not replenish by drinking water. You can mimic this cooling effect by spraying the skin with water when you are hot.
The lowest layer of skin, the hypodermis, provides an insulating layer to maintain heat.
2. Protection.
The skin is a physical barrier that prevents not only bacteria, viruses, and fungi from entering the body but also keeps most environmental toxins out of your body, including allergens. Yes, you may have heard differently, but the skin absorbs very little of what goes on it. This is what we refer to as the Skin Barrier Function and is probably the most important function of skin.
The skin barrier function can become damaged in a number of ways; excessive exfoliation, exposure to dry air and the environment, exposure to sun, etc. Damage to the skin barrier can result in redness, burning sensations, sensitive skin, rashes and breakouts as well as making one more susceptible to infections and allergies.
Besides protecting the body from things entering it also prevents water from leaving the body to prevent dehydration. So you can see why protecting and repairing the skin barrier function is vital. Look for more blogs about the skin barrier.
3. Sensation.
As a sensory organ, the skin helps you evaluate the outside environment. One reason for this is to help you decide whether or not to wear a coat. Besides temperature, receptors in the skin relay information on pain and pressure. In some cases this can be very enjoyable, even sexual.
4. Excretion.
Enzymes in the skin help to break down toxins. Those, along with normal by products of biochemistry are secreted through the skin by sweating. This helps remove wastes from the body.
5. Immunity.
Cells in the skin play important roles in the immune system to combat infection. Part of this role involves inflammation to protect the rest of the body from potential pathogens.
6. Endocrine gland.
Endocrine glands make hormones and vitamin D is considered a hormone. A precursor to vitamin D, known as 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) is made in the skin. This precursor is converted to Vitamin D3 with exposure to sunlight where it then goes to the liver for additional processing. Vitamin D is important for the absorption of calcium from the intestines as well as other less defined roles.
Colorado Aromatics products are formulated to help the skin perform these important roles of the body and keep you healthy. I hope you can see why it is important to keep your skin healthy. We cannot survive without healthy skin.


Great synopsis of why our skin is so important.
Skin is incredibly fascinating! Treat yours well!
It makes sense that your skin barrier helps your body by preventing it from getting dehydrated. My wife has been noticing that she has started to become dehydrated ever since the weather started getting warmer, and she is worried that her skin may be to blame since she drinks water every day before work. Maybe she should see a dermatologist that can help make sure that her skin is healthy.